Architecture & WEB Server integration
Part 1 : VPC & Security Group
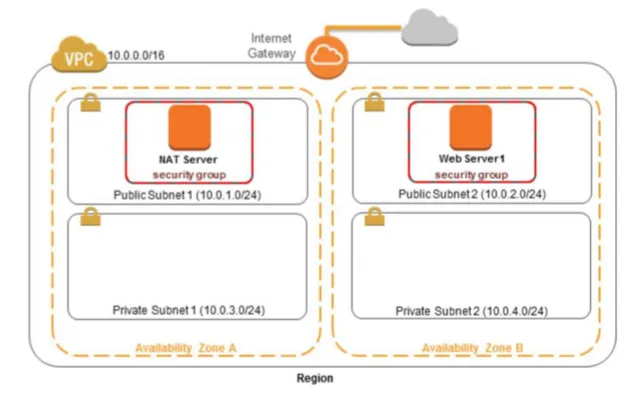
Architecture
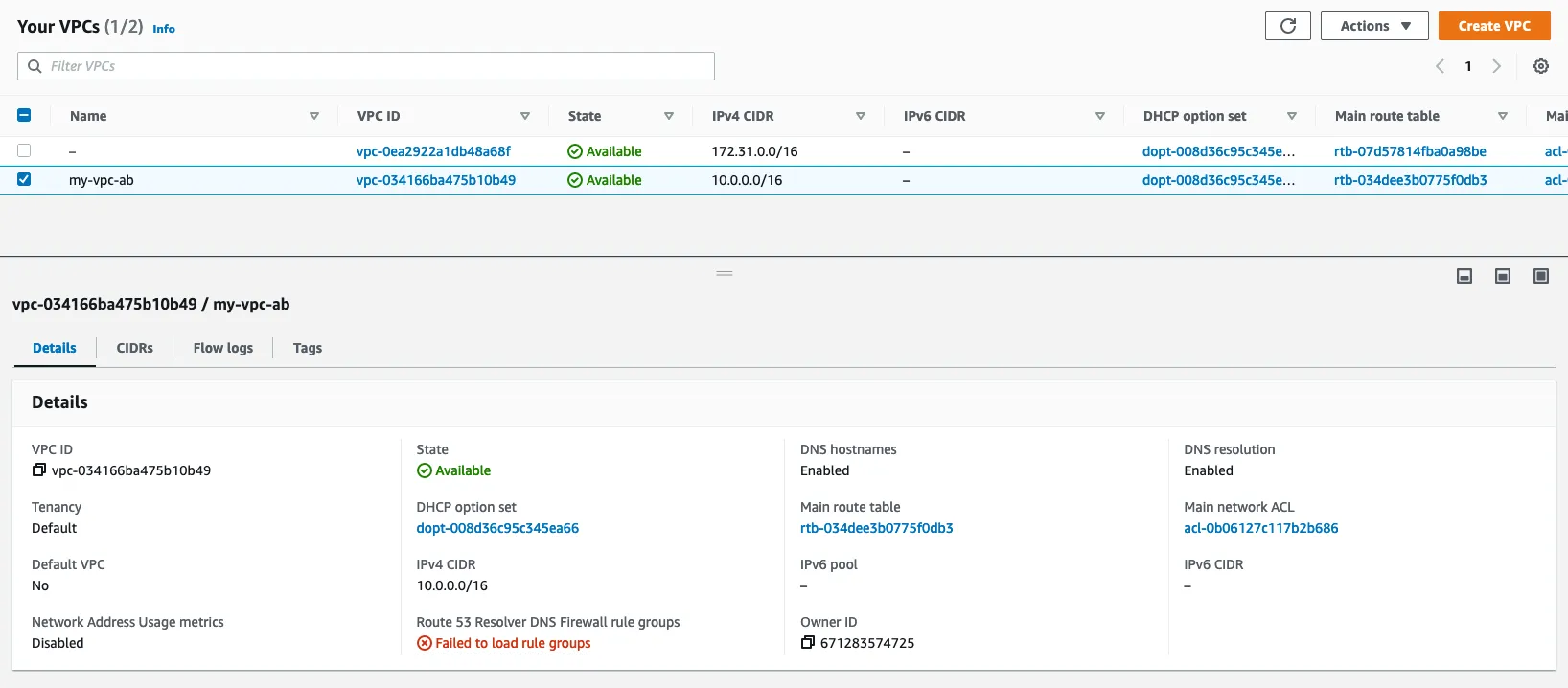
1.1 : Create a VPC
With Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), you can launch AWS resources in a logically isolated virtual network that you’ve defined. This virtual network closely resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS.
name : my_vpc_ab
1.2 : Create a Gateway
An internet gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that allows communication between your VPC and the internet. It supports IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
name : my_igw_ab

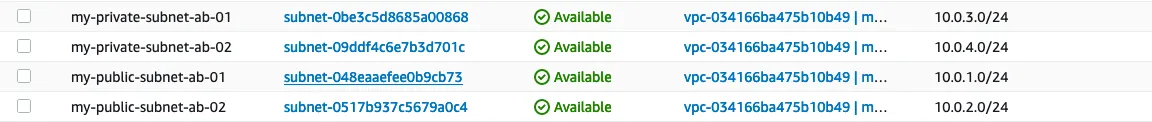
1.3 : Create a Subnet
A subnet is a range of IP addresses in your VPC. You can create AWS resources, such as EC2 instances, in specific subnets.
names :
- my_private_subnet_ab-01
- my_private_subnet_ab-02
- my_public_subnet_ab-01
- my_public_subnet_ab-02
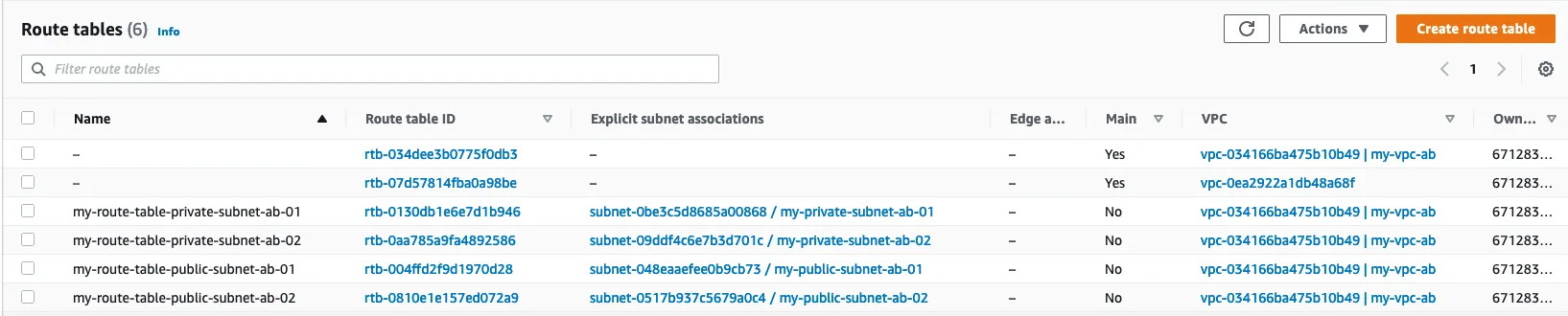
1.4 : Create a Route Table
A route table contains a set of rules, called routes, that determine where network traffic from your subnet or gateway is directed.
names :
- my_route_table_private_subnet_ab-01
- my_route_table_private_subnet_ab-02
- my_route_table_public_subnet_ab-01
- my_route_table_public_subnet_ab-02
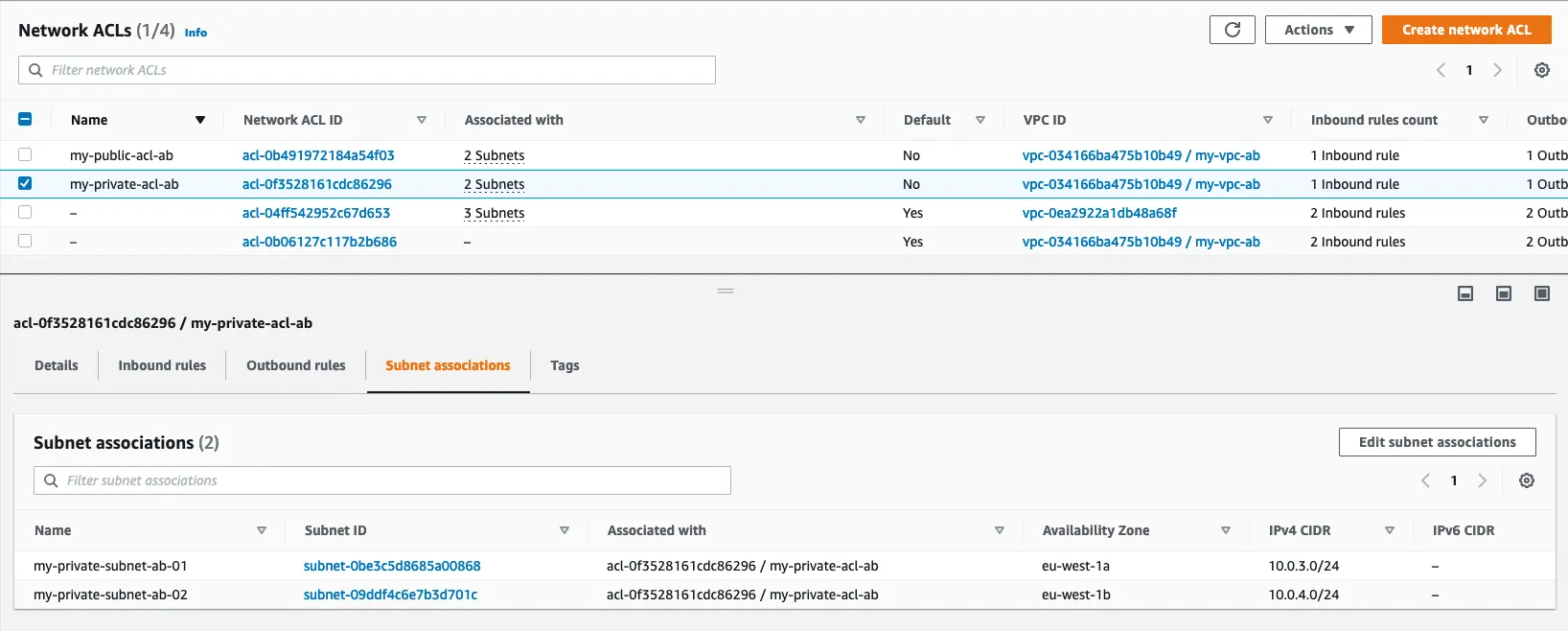
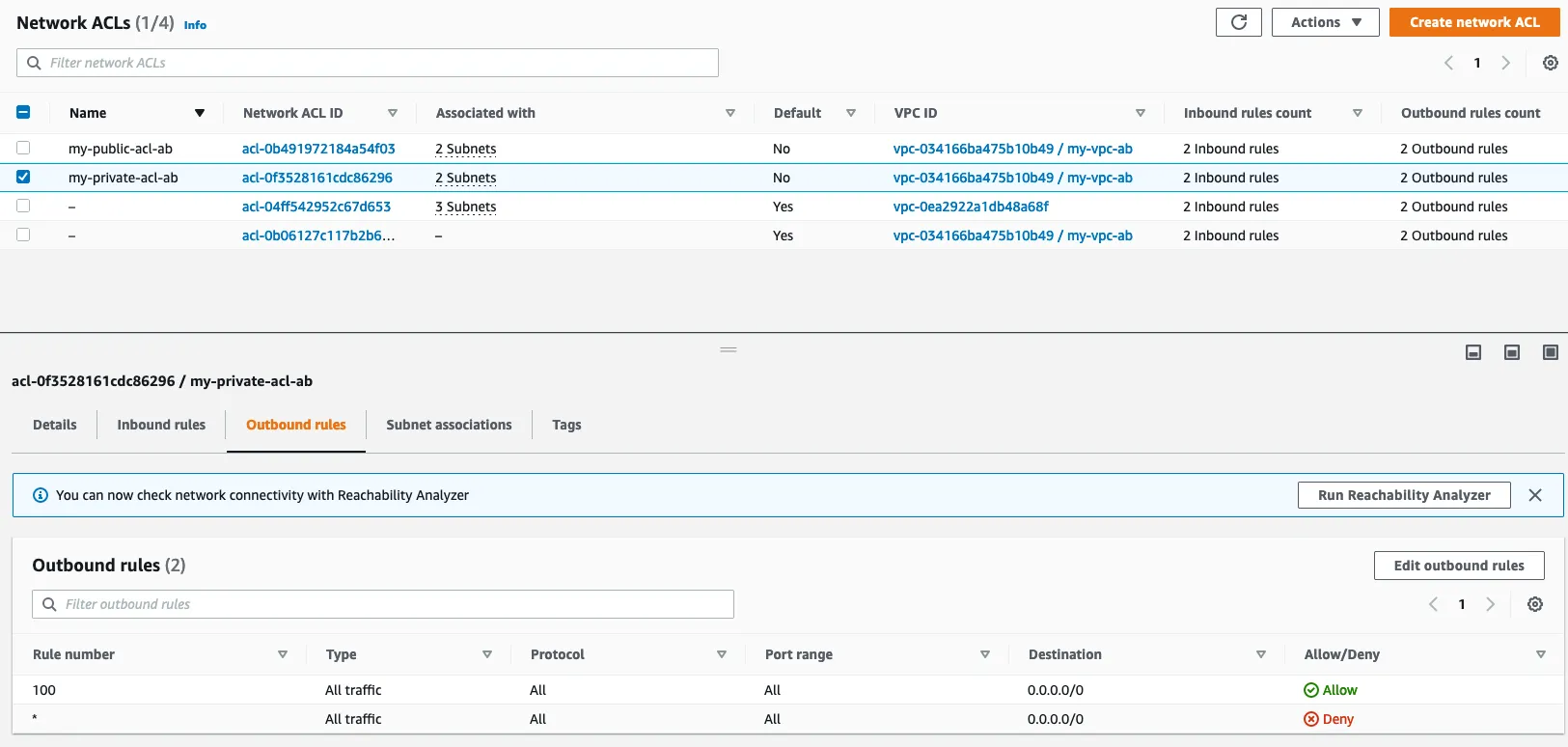
1.5 : Create ACL
A network access control list (ACL) allows or denies specific inbound or outbound traffic at the subnet level. You can use the default network ACL for your VPC, or you can create a custom network ACL for your VPC with rules that are similar to the rules for your security groups in order to add an additional layer of security to your VPC.
- my_private_acl_ab
- my_public_acl_ab
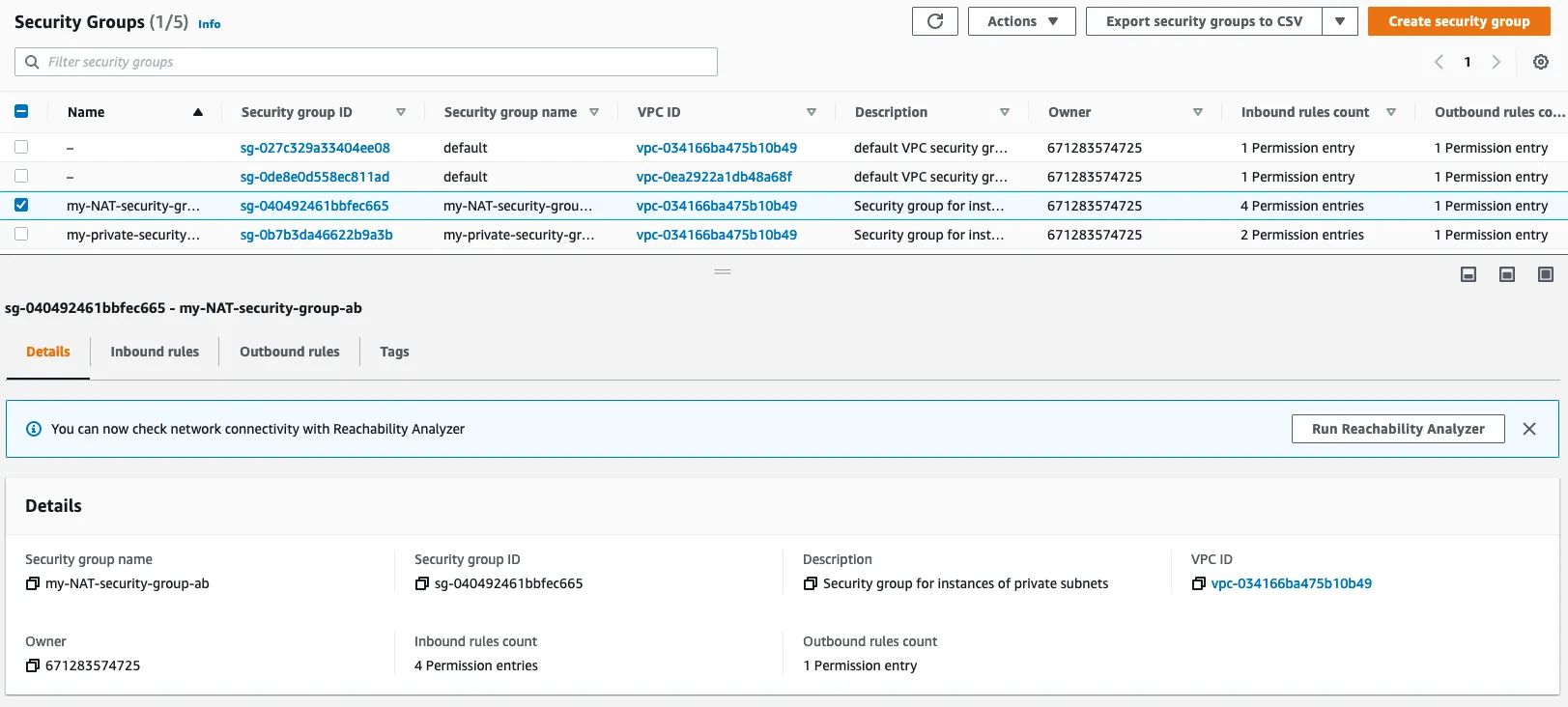
1.6 : Create a Security Group
A security group controls the traffic that is allowed to reach and leave the resources that it is associated with. For example, after you associate a security group with an EC2 instance, it controls the inbound and outbound traffic for the instance.
names :
- my_private_security_group_ab
- my_public_security_group_ab
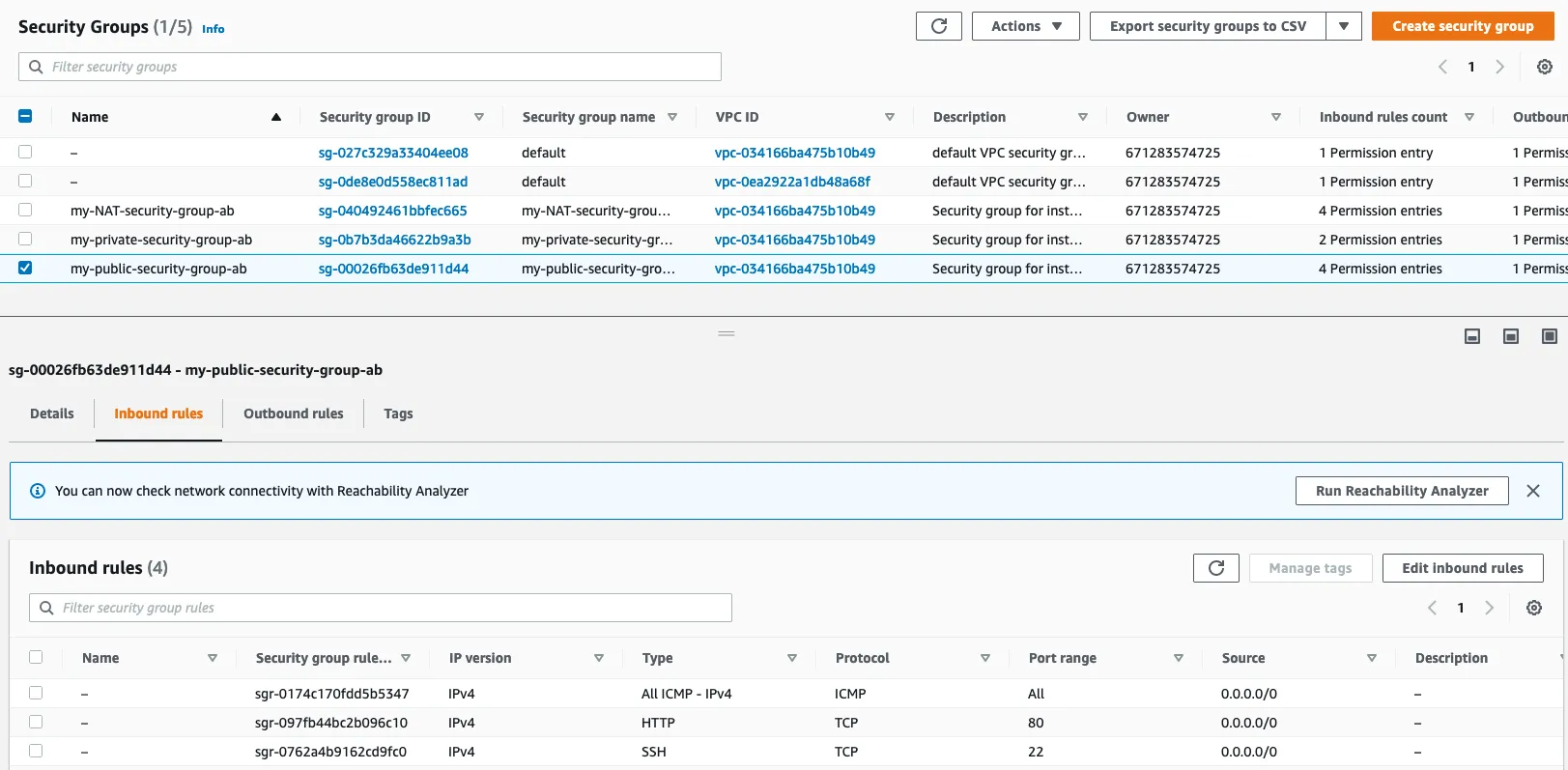
1.7 : Create a AMI
name : serveur-web-instance-ab
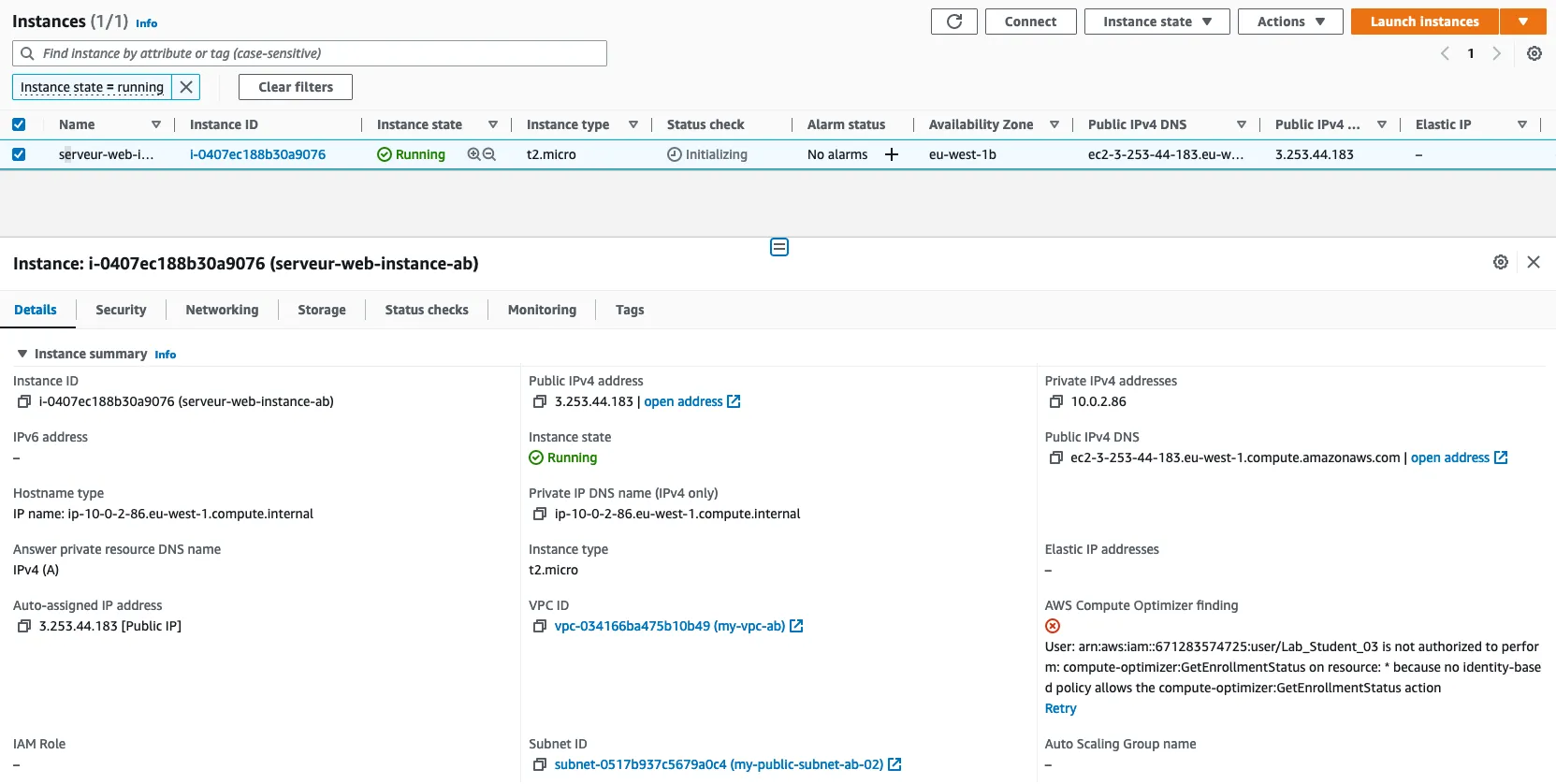
ssh connection to the AMI :
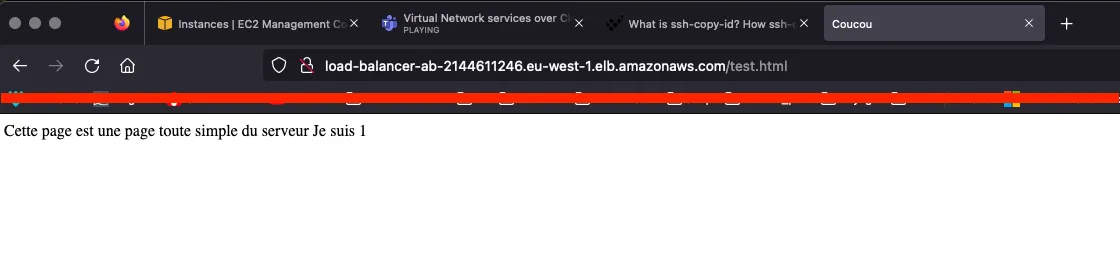
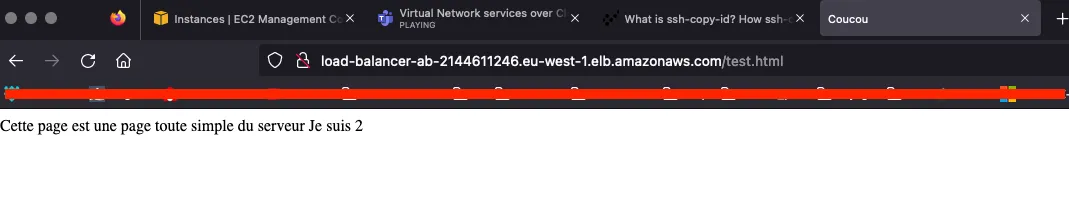
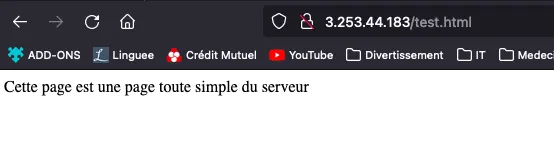
Pages result (test.html & ping.html) :
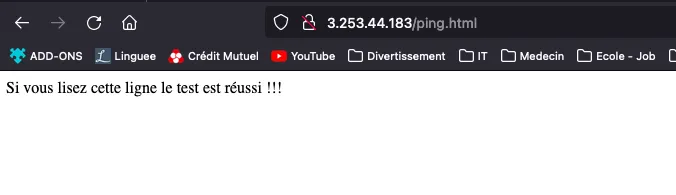
1.8 : Create a NAT security group
1.9 : Create a NAT Instance as Bastion
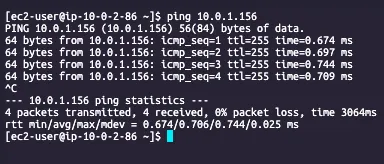
A bastion is a server that is accessible from the internet and that is used to access a private network. It is a security best practice to use a bastion to access a private network.
Ping result :
Part 2 : Load Balancer & Auto Scaling
AWS Architecture

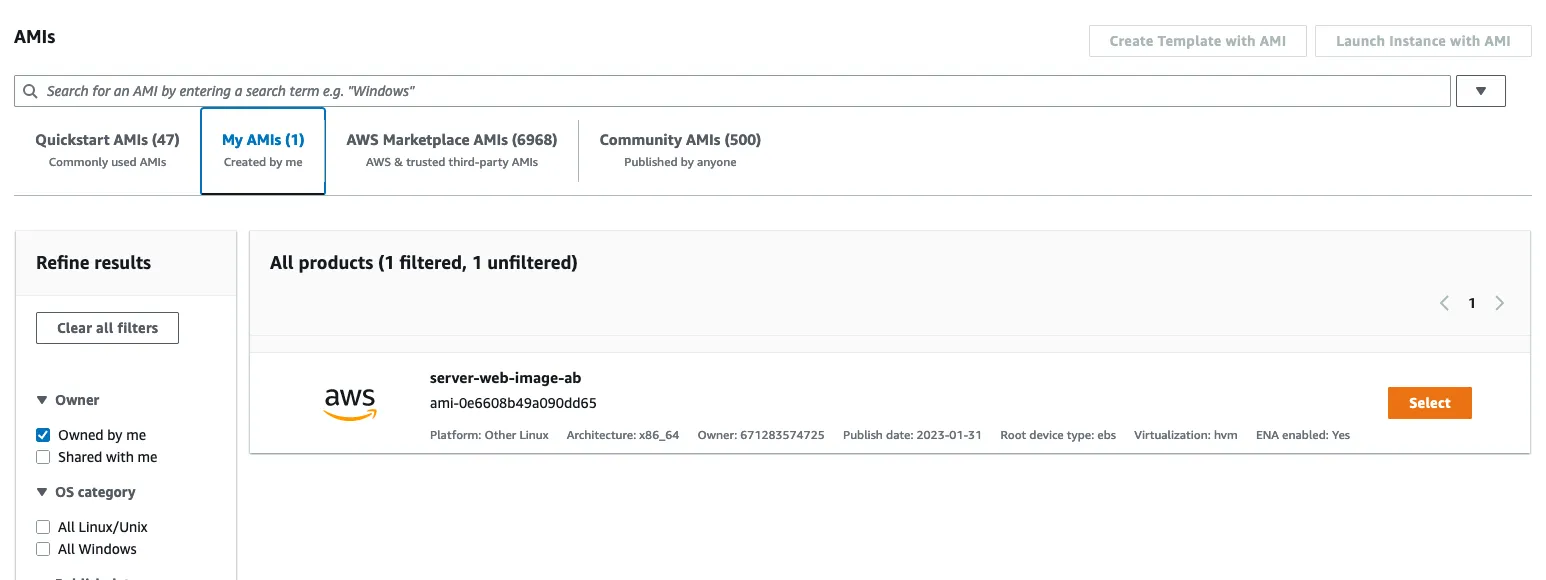
2.1 : Create a AMI
Create a AMI from the web server instance created in part 1.7
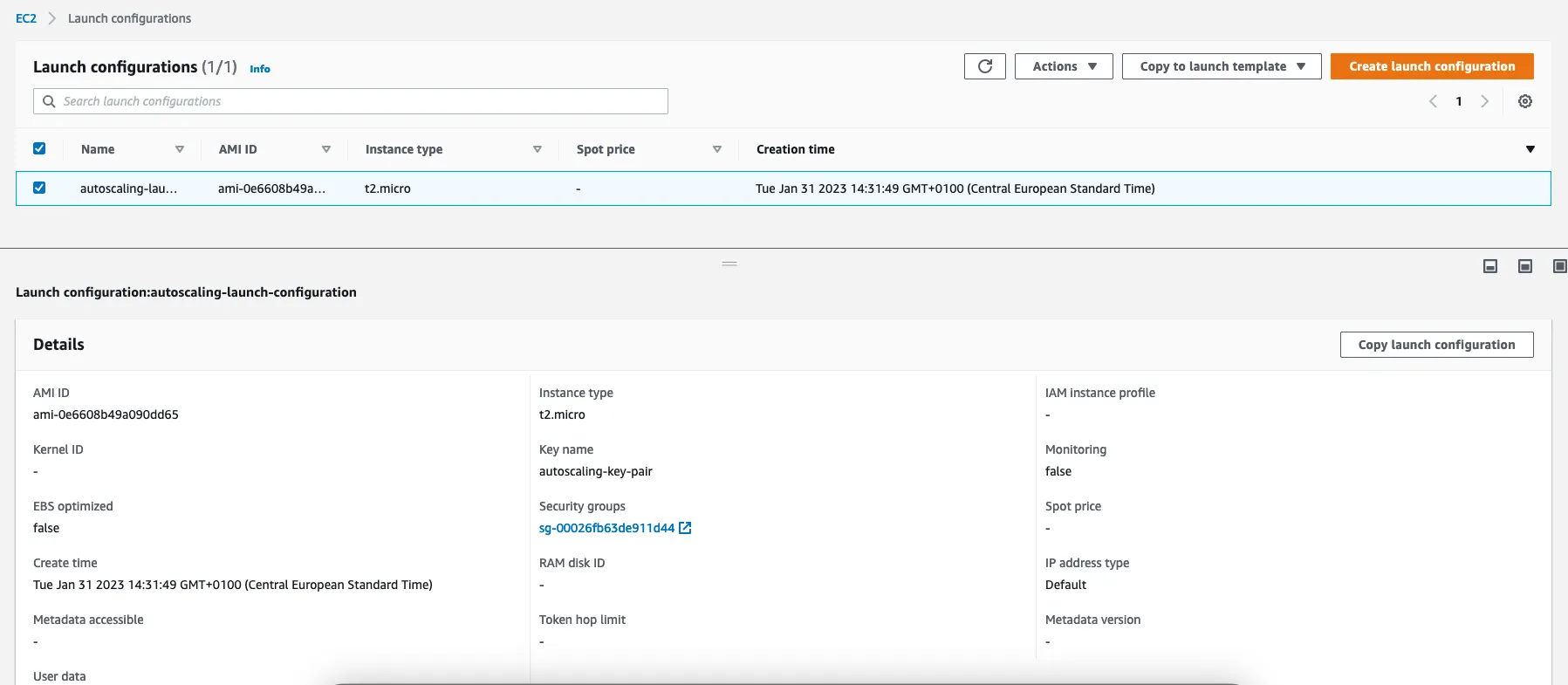
2.2 : Create a configuration template
name : autoscaling_launch_configuration_ab
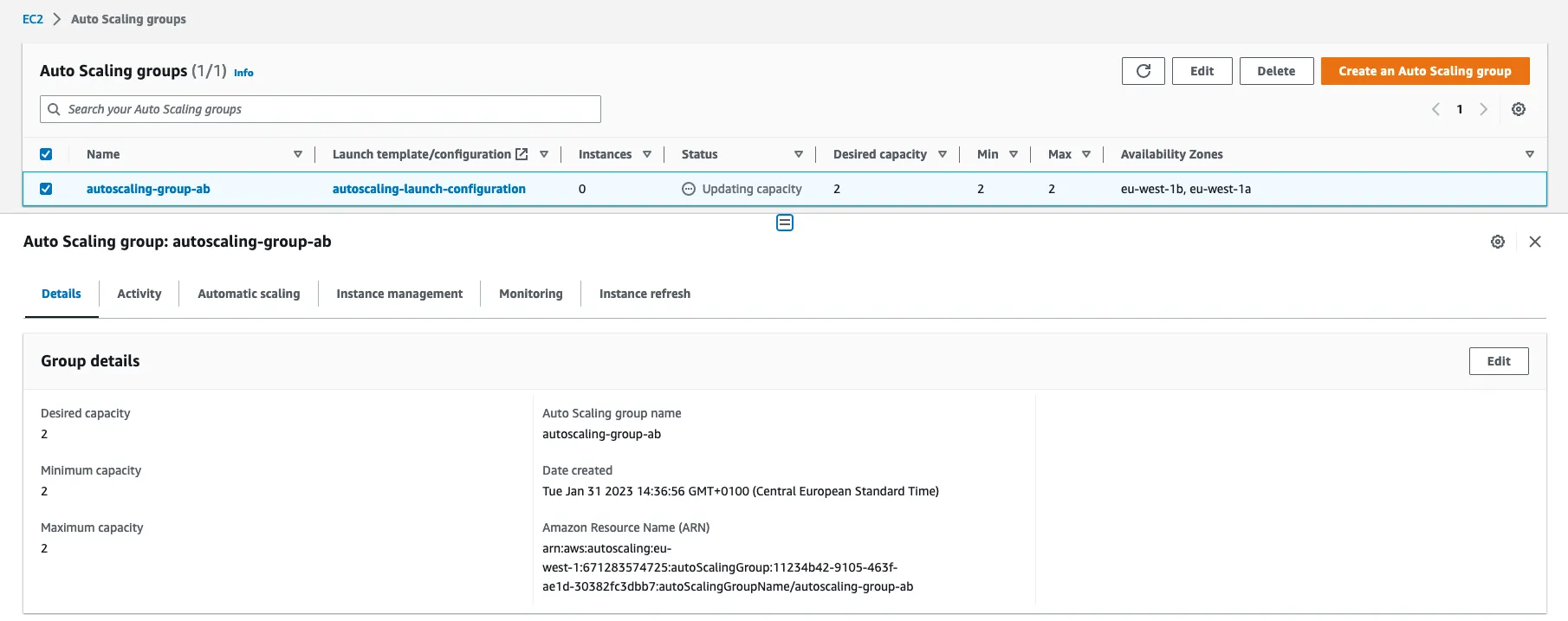
2.3 : Create a Auto Scaling Group
An Auto Scaling group contains a collection of EC2 instances that are treated as a logical grouping for the purposes of automatic scaling and management.
name : autoscaling_group_ab
Configuration with 2 instances MIN/MAX
Instance creation verification :
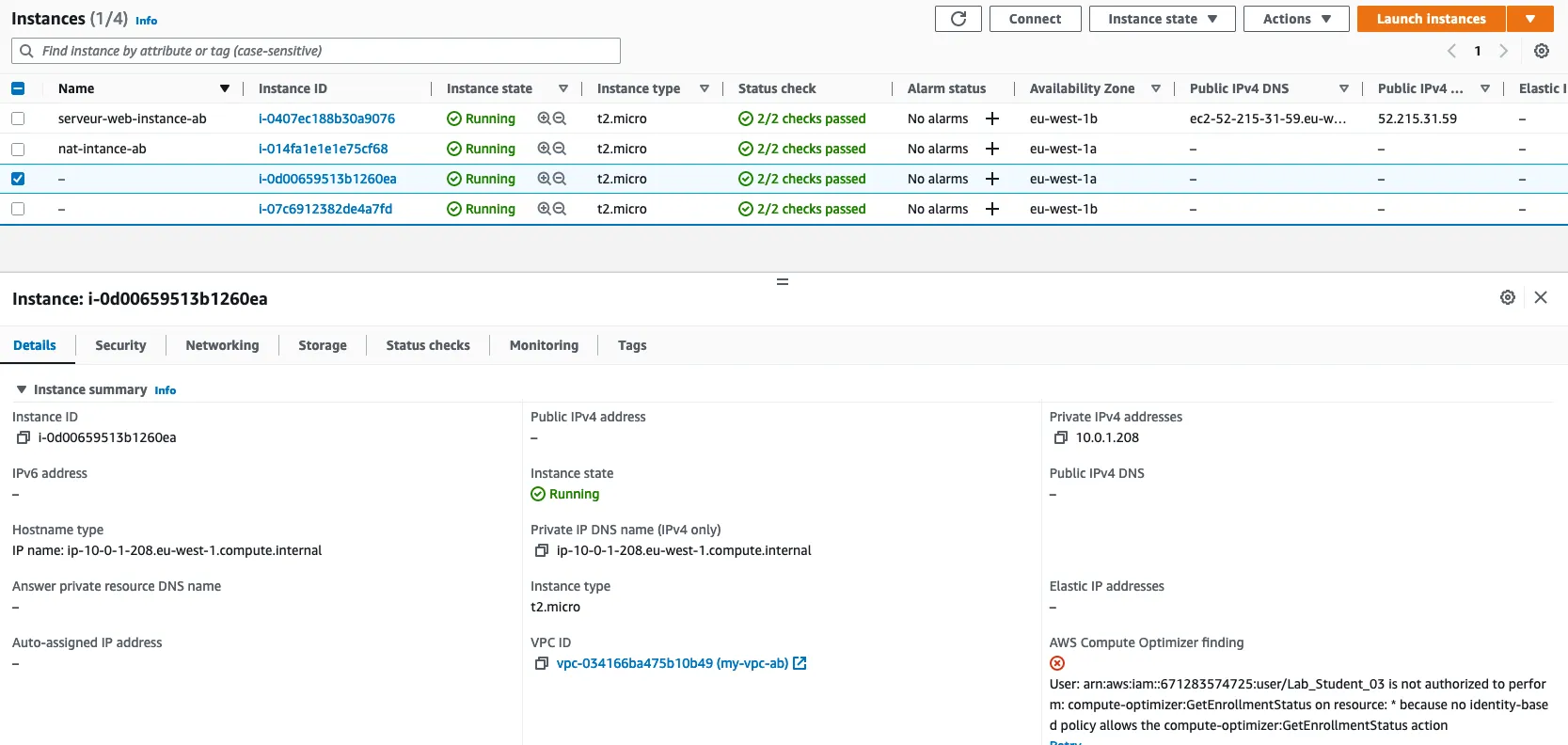

Try to delete one instance :
a new instance has been created

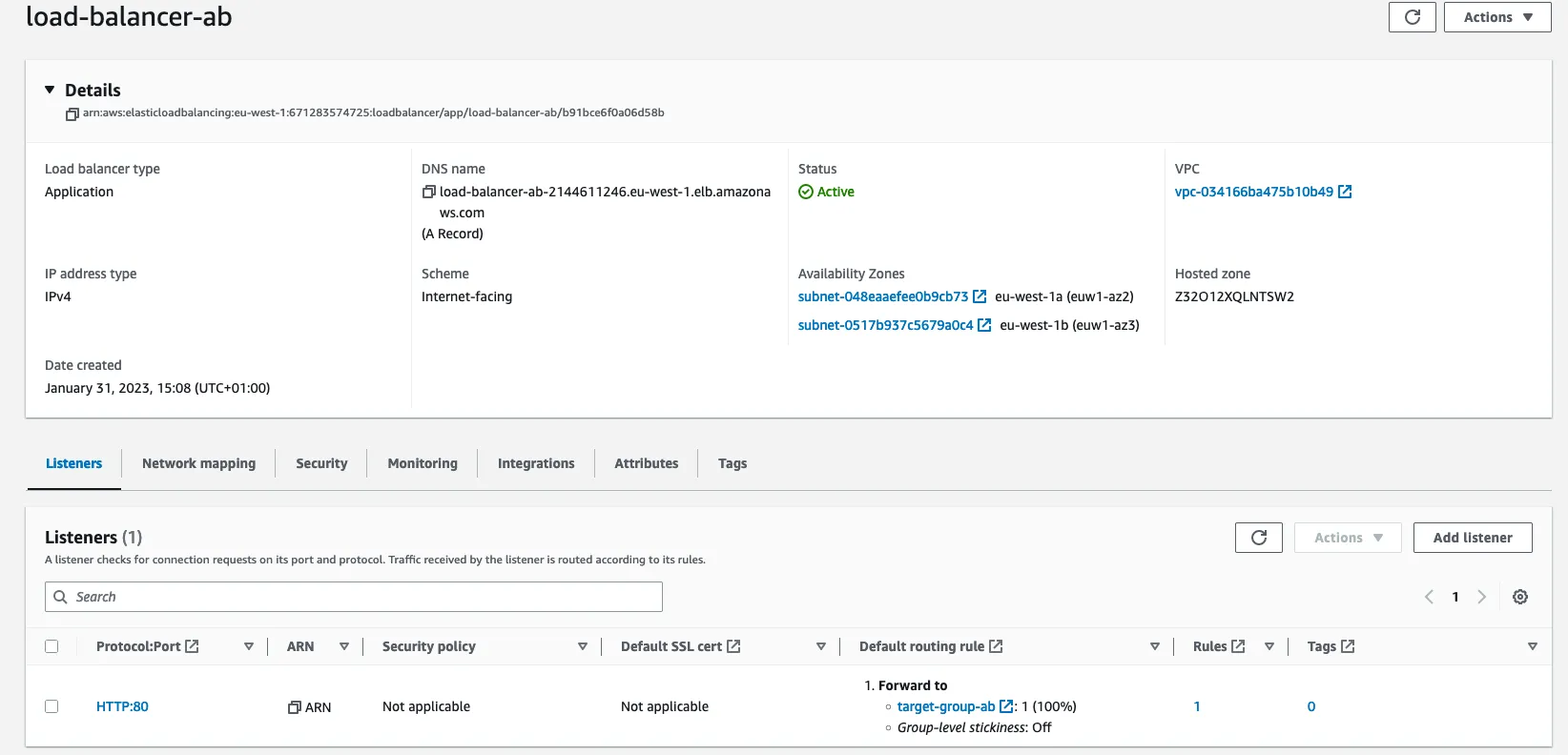
2.4 : Create a Load Balancer
Load balancing is the method of distributing network traffic equally across a pool of resources that support an application.
name : load_balancer_ab
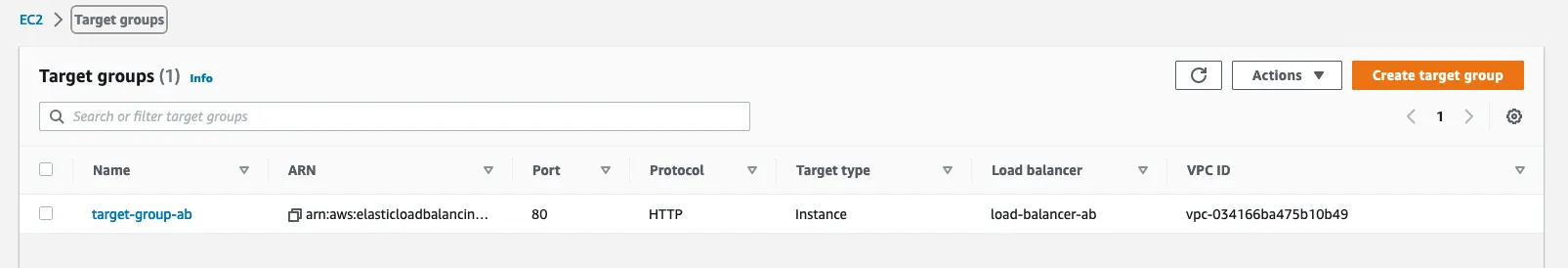
target group creation :
Each target group is used to route requests to one or more registered targets. When you create each listener rule, you specify a target group and conditions.
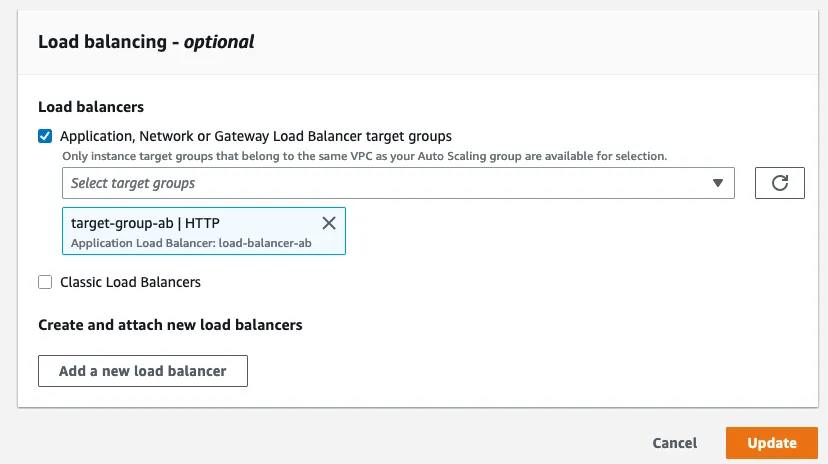
2.5 : Add Target Group to Load Balancer
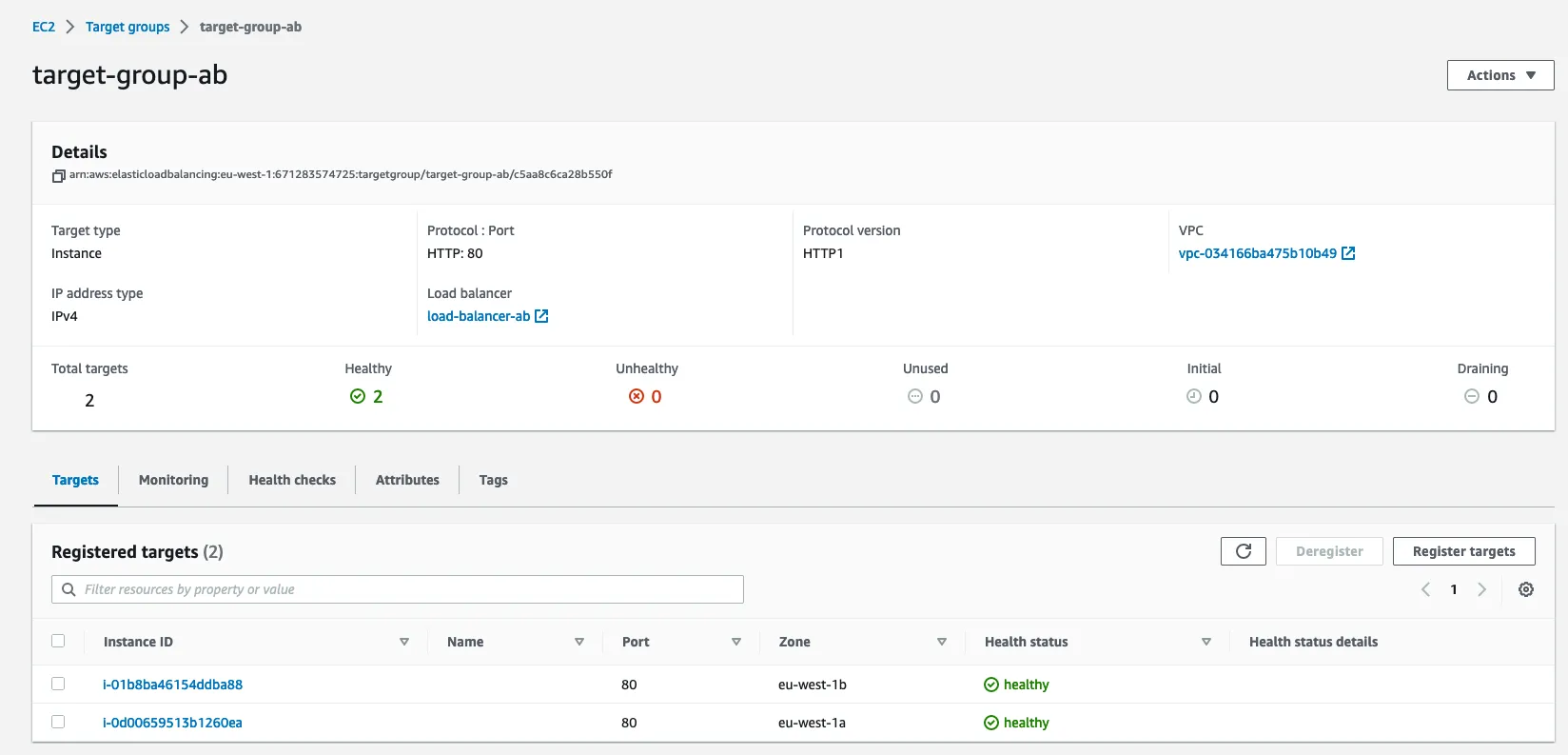
Health check :
2.6 : Test Load Balancer
After customizing the test.html page, we can test the load balancer :